Has any country thought about joining NATO? NATO, or the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, is a political and military alliance of 30 North American and European countries. But it’s more complex than filling out a form and sending it in. There are specific requirements that countries need to meet to join this prestigious alliance. This blog post will outline those requirements, so you’ll understand precisely what it takes to become a member of NATO.
Brief History of NATO
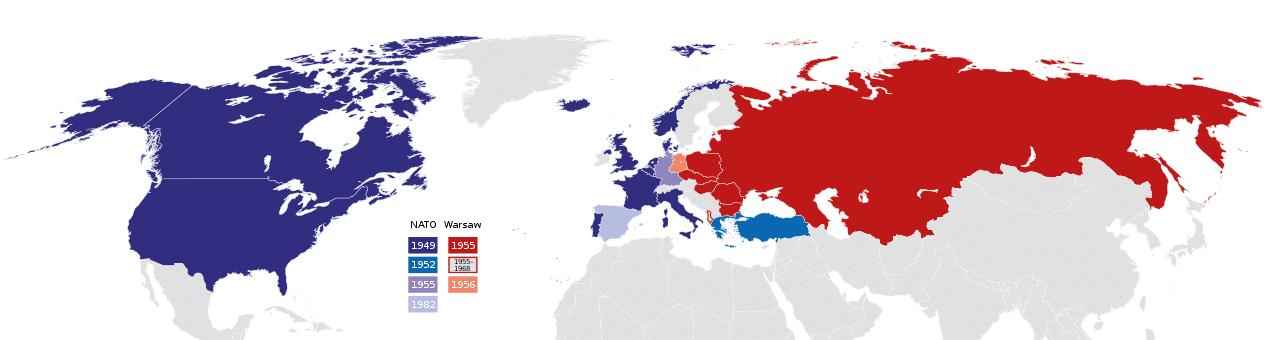
NATO, which stands for the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, was established in 1949. It was formed as a response to the rising tensions and security concerns following World War II. The initial members of NATO included twelve countries from North America and Europe.
The founding of NATO marked a significant turning point in international cooperation. Its creation aimed to promote collective defense and prevent the outbreak of another devastating conflict. By forming a mutual defense alliance, member countries sought to deter potential aggressors and maintain peace in the North Atlantic region.
Purpose of NATO
The primary purpose of NATO is to ensure the collective defense and security of its member nations. This is achieved through a commitment to mutual assistance in the event of an armed attack on any member state. The alliance is based on the principle of solidarity, with each member pledging to come to the defense of others if they are attacked.
NATO operates on the principle of shared responsibilities and burdens. It provides a platform for member countries to consult and cooperate on defense and security matters. Through joint military exercises, intelligence sharing, and policy coordination, NATO enhances the effectiveness and interoperability of its member states’ armed forces.
Furthermore, NATO serves as a forum for political dialogue and cooperation among its members. It provides a platform for discussing common challenges, fostering trust, and building partnerships beyond the alliance. NATO’s partnerships with countries outside the alliance contribute to regional and global stability.
In summary, NATO’s purpose is to safeguard security and promote the common values of its member nations through collective defense, political dialogue, and cooperation.
Membership Requirements for NATO
In order to join NATO, countries must meet certain membership requirements. These requirements are put in place to ensure that new members are able to contribute effectively to the alliance’s goals and objectives. In this section, we will explore the key criteria that countries need to meet in order to become NATO members.
Geographical Location
Geographical location plays a vital role in the process of joining NATO. According to Article 10 of the North Atlantic Treaty, only countries situated in the North Atlantic area can become members of the alliance. This geographical limitation ensures that NATO remains focused on its core mission of collective defense in the Euro-Atlantic region.
Political Stability
Political stability is another important factor that NATO considers when evaluating prospective members. The alliance seeks countries with stable political systems, functioning institutions, and a commitment to democratic values. This requirement ensures that new members have the necessary stability to contribute to NATO’s decision-making processes and uphold its principles.
Democracy and the Rule of Law
NATO places a strong emphasis on democracy and the rule of law. Prospective members must demonstrate a firm commitment to democratic governance, including respect for human rights, freedom of speech, and the independence of the judiciary. Upholding democratic values is crucial in ensuring that NATO remains a community of like-minded nations that share common principles.
Defense Spending
Defense spending is a key indicator of a country’s commitment to its own security and defense capabilities. NATO expects its member states to allocate a certain percentage of their GDP to defense expenditures. Currently, the guideline is for member countries to aim for a defense spending target of 2% of GDP. This requirement ensures that new members are willing and able to contribute their fair share to the alliance’s collective defense efforts.
Commitment to Collective Defense
Perhaps the most important requirement for NATO membership is a commitment to collective defense. This means that countries seeking to join the alliance must be willing to come to the aid of other member states if they are attacked. Additionally, they must be willing to contribute to NATO’s missions and operations, both in terms of military capabilities and resources. This requirement highlights the importance of solidarity and mutual support among NATO members.
In conclusion, joining NATO requires countries to meet several membership requirements. These include meeting the geographical criteria, demonstrating political stability, upholding democratic values, allocating a sufficient amount of defense spending, and committing to collective defense. By fulfilling these requirements, countries can become valuable contributors to the alliance’s mission of ensuring the security and stability of the Euro-Atlantic region.
Process of Joining NATO
Joining NATO is a meticulous and multistep process that requires careful planning and coordination. In this section, we will explore the various steps involved in becoming a member of this esteemed organization. From contacting the NATO Liaison Office to the evaluation and decision-making process, each stage plays a crucial role in determining a country’s eligibility and readiness for NATO membership.
Contacting the NATO Liaison Office
The initial step in the process of joining NATO is to establish contact with the NATO Liaison Office. This office serves as the primary point of contact for countries interested in becoming members. By reaching out to the office, the aspiring member state expresses its intent and initiates the formal procedure for joining NATO. This communication is essential as it allows NATO to provide guidance and support throughout the membership application process.
Submission of Membership Application
Once contact has been established, the aspiring member state must submit a formal membership application to NATO. This application provides an opportunity for the country to outline its reasons for seeking NATO membership and to showcase its commitment to the principles and values upheld by the alliance. The application should address various aspects, such as political, economic, and military readiness, as well as the country’s ability to contribute to NATO’s collective defense and security efforts.
Membership Action Plan (MAP)
If the membership application meets the necessary criteria, the aspiring member state may be invited to participate in the Membership Action Plan (MAP). The MAP serves as a framework that assists countries in preparing for NATO membership. It involves a comprehensive assessment of the country’s capabilities, institutions, and policies, with the aim of identifying areas that may require further development or reform. The MAP provides guidance and support to the aspiring member state, enabling it to align its structures and policies with NATO standards.
Evaluation and Decision-Making Process
Following the completion of the MAP, the aspiring member state enters the evaluation and decision-making phase. During this stage, NATO conducts a thorough assessment of the country’s progress and readiness for membership. This evaluation includes an examination of the aspiring member’s political, economic, and military capabilities, as well as its commitment to democratic values, human rights, and the rule of law.
Based on the evaluation, NATO member states engage in a collective decision-making process to determine whether the aspiring member state fulfills the necessary criteria for membership. This decision is made with careful consideration of the aspiring member’s commitment to NATO’s principles, its contributions to collective defense, and its ability to enhance the security of the alliance as a whole.
Benefits of Joining NATO
As a member of NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization), countries enjoy numerous benefits that contribute to their enhanced security, defense cooperation, political and economic stability, as well as access to invaluable resources and expertise. In this section, we will delve into the key advantages that nations gain by joining NATO.
Enhanced Security and Defense Cooperation
Joining NATO provides countries with a framework for enhanced security and defense cooperation. By becoming a member, nations can rely on the collective strength of the alliance to deter potential adversaries and protect their sovereignty. The principle of collective defense ensures that an attack on one member is seen as an attack on all, fostering a sense of solidarity and shared responsibility among allies. This cooperative approach to security significantly strengthens a country’s defense capabilities, ensuring a robust and unified response in the face of potential threats.
Collective Defense and Deterrence
One of the fundamental principles of NATO is collective defense. This means that if a member state is attacked, all other members are obligated to come to its defense. This commitment ensures that nations can rely on the support of their allies in times of need, providing a powerful deterrent against potential aggressors. By joining NATO, countries can benefit from the security guarantees that come with collective defense, which in turn contributes to regional stability and peace.
Political and Economic Stability
Membership in NATO brings not only military security but also political and economic stability. The alliance serves as a platform for political dialogue and cooperation among member states, fostering trust and understanding. Through regular consultations and joint decision-making, nations can address common challenges and work towards shared goals, promoting stability within the alliance and beyond. Additionally, NATO membership can attract foreign investment, boost economic growth, and provide access to a vast network of trade partners, creating favorable conditions for economic prosperity.
Access to NATO Resources and Expertise
Joining NATO grants countries access to a wealth of resources and expertise. The alliance offers a wide range of capabilities, including intelligence sharing, military training and exercises, and access to advanced technologies. Members can tap into NATO’s vast network of experts and benefit from their knowledge and experience in areas such as defense planning, crisis management, and counterterrorism. This access to resources and expertise strengthens a country’s defense capabilities and enhances its ability to respond effectively to emerging security challenges.
The benefits of joining NATO extend far beyond mere military cooperation. Enhanced security, collective defense, political and economic stability, as well as access to valuable resources and expertise, make NATO membership an attractive proposition for countries seeking to strengthen their position on the global stage.
Current NATO Member Countries
NATO, or the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, is an intergovernmental military alliance that was founded in 1949. It was established with the aim of promoting peace and security among its member countries through collective defense. Over the years, NATO has expanded its membership to include various nations from different regions of the world. In this section, we will explore the current NATO member countries, their date of joining NATO, and a brief overview of their membership process.
List of NATO Member Countries
As of 2021, the NATO Alliance consists of 30 member countries. Here is a list of the current NATO member countries:
- Albania
- Belgium
- Bulgaria
- Canada
- Croatia
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Italy
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- North Macedonia
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Turkey
- United Kingdom
- United States
- Finland
Date of Joining NATO
Each member country joined NATO at different times, reflecting the organization’s expansion and evolving geopolitical landscape. Here are the dates when some of the current NATO member countries joined the alliance:
- Albania: Joined on April 1, 2009
- Canada: Joined on April 4, 1949
- Germany: Joined on May 9, 1955
- Greece: Joined on February 18, 1952
- Italy: Joined on April 4, 1949
- United States: Joined on April 4, 1949
Please note that the dates mentioned above are just a few examples, and the rest of the member countries joined NATO at different points in time.
Brief Overview of Their Membership Process
The process of becoming a NATO member involves various steps, including political, economic, and military criteria. Here is a brief overview of the membership process:
- Political Criteria: Prospective member countries must demonstrate a commitment to democracy, the rule of law, individual liberty, human rights, and the peaceful resolution of conflicts. They are expected to have stable democratic institutions and respect for minority rights.
- Economic Criteria: The economic aspect of NATO membership involves having a functioning market economy and the capacity to contribute to the alliance’s common defense efforts. Member countries are encouraged to promote economic prosperity and stability.
- Military Criteria: NATO member countries should have capable and interoperable armed forces that can contribute effectively to collective defense and NATO-led operations. They are expected to invest in defense capabilities and commit to maintaining a certain level of defense spending.
- Invitation to Join: After a thorough evaluation process, existing NATO member countries assess the readiness and compatibility of a prospective member. If a consensus is reached among the member countries, an invitation is extended to the aspiring nation to join NATO.
- Ratification: The aspiring country then needs to go through the process of ratification, which involves approval from its own government and, in some cases, a referendum. Once ratified, the country officially becomes a NATO member.
It’s important to note that becoming a NATO member is a voluntary decision made by each sovereign nation, and the membership process can vary in duration and complexity for different countries.
NATO is an alliance that comprises 30 member countries, each with a unique journey of joining the organization. The membership process involves meeting political, economic, and military criteria, followed by an invitation and subsequent ratification. NATO membership symbolizes a commitment to collective security and cooperation among nations, aiming to ensure peace and stability in the North Atlantic region and beyond.
The Bottom Line
In conclusion, joining NATO requires meeting certain criteria and fulfilling specific obligations. The process begins with demonstrating a commitment to democratic values, the rule of law, and respect for human rights. Furthermore, aspiring member countries must have stable institutions, a functioning market economy, and the ability to contribute to the alliance’s collective defense capabilities. A formal invitation from existing NATO members is necessary to embark on the accession process. Once invited, potential members must undergo a thorough evaluation by NATO’s experts and demonstrate their ability to align their defense policies and capabilities with those of the alliance. Finally, the approval of all current NATO members is required before a country can officially join the alliance. Joining NATO is a significant step towards enhancing regional security and promoting stability, and it reflects a nation’s commitment to collective defense and international cooperation.
Related Articles
10 Best Handguns for Self-Defense
When it comes to...
The Truth About Sanctions: Why Don’t They “Work”?
In 2022,...
History of Israel-Palestine Conflict
Israel and...
After the WAR initiated by HAMAS on October 7th, the Middle East will not be the same
On the -th of...
The Israeli army is prepared for an offensive on the Gaza Strip, involving attacks from “air, sea, and land.”
The IDF (Israel...
War in Israel: Current Developments – Video
Rafah...
Russia vs USA: Who Would Win in a Potential War?
In the...
NATO vs China: Who Would Win in a Potential War?
In the realm of...
11 Best Assault Rifles in the World
Welcome to a world...
Yevgeny Prigozhin (Wagner founder) is dead
According...
Terrifying Realities of a Potential Nuclear War
The Devastating...
What to Do in Case of a Nuclear Attack
What to Do in Case...
11 Strongest and Most Powerful Navies in the World
When it comes to...
The Most Powerful Nuclear Weapons
The sheer power...
Understanding the Nature of War – The Clash of Wills
War is the...
Ukrainian Defense Forces Celebrate One-Year Anniversary of Kherson Region Liberation
Around one year...
Prigozhin First Video Speech After Unsuccessful Uprising
Following a recent...
11 Best Sniper Rifles in the World
Important Factors...
What is Russia saying about the war in Ukraine, Episode 1
Did you ever...
13 Most Powerful Weapons in the World
Weapons of immense...
What is Happening in Russia, Episode 3
Welcome to the...
What is Happening in Russia, Episode 2
Have you ever...
10 Strongest Tanks in the World
Tanks represent...
10 Strongest Armies in the World
When it comes to...
Putin: We cannot stop the fire when they advance on us!
Putin ten...
10 Best Air Defence Systems in the World
Image:...
Alexei Navalny Letters From Prison
Image:...
Ukraine’s Struggle for Survival and Western Dependency
Ukraine has long...
What is Happening in Russia, Episode 1
Have you ever...
10 Strongest Fighter Jets in the World
Image:...
10 Strongest NATO Members
Image:...
Mobilized Soldiers Expose Dire Conditions and Neglect in Deployment to Luhansk
source:...
Why is everything so poor and sad in Russia?
Image:...
Tensions Escalate in Northern Kosovo as Serbian President Mobilizes Army
Image:...
Putin’s Russia and the Need for a Fresh Security Approach in Europe
Image:...
DeSantis Declares Presidential Bid with Elon Musk
Image:...
Russian military personnel shelled the Zaporizhia Nuclear Power Plant
Image:...
Prigozhin Revelations The Truth Behind the Capture of Bakhmut
Image:...
President Zelensky Visit G7 Turning Point in Russia-Ukraine War
Image:...
Turning a Blind Eye No More: Zelensky’s Bold Stand Against Crimean Annexation
Unfortunately,...
Navigating the Fluidity of War and Geography: Insights and Strategies
War is Geography:...
Latest Updates on Russian Invaders’ Activities in Occupied Territories
Russian Invaders...
US Denies Ukrainian Pilots Training on F-16 Fighter Jets
Complexities of...
West Strong Support for Ukraine’s Recovery and Containment of Russia
Kremlin's Failed...
Ukraine Supreme Court Chairman Confronts Allegations of Blatant Bribery
Vsevolod Knyazev...
Gold Coin Treasure from Alexander the Great Era found in Annexed Crimea
Crimea's Hidden...
Rishi Sunak Hails Zelenskyy as a Modern-Day Churchill
Volodymyr...
The Moral Factor in War: Ukraine’s Key to Victory
"We were actively...
The West’s Triumph in the New Cold War: Technology of Freedom Wins Out
The Chinese leader...
The Illusion of Power: How Putin’s Russia is Making the Same Mistakes as its Past Leaders
Modern Russia and...